EMETICS
Emetics are the agents which when taken orally or by injection induce/evoke the vomiting.
Mechanism of action– It generally act by two ways :-
- By stimulation of chemoreceptor trigger zone(CTZ) located in the area of postrema medulla oblongata in brain.
- By local irritating effect on GIT. E.g. copper sulphate, sodium chloride, zinc sulphate, antimony potassium tartrate.
Contraindications- Emetics should not be used in conditions like:-
- Significant CNS depression and shock.
- Unconscious or semi-consciousness or coma situations.
- Patient with severe heart disease.
- In tuberculosis, anemia and advanced pregnancy.
- Poisoning caused by corrosive or petroleum product.
Applications:-
1.Mechanical antidote
2.Sometimes emetics are added in cough preparations in low dose to stimulate the flow of respiratory tract.
Some of the common Emetics are :-
COPPER SULPHATE
Mol. Formula- CuSo4.5H2O
Mol. Wt.- 249.7gm
Synonyms:- Blue vitriol, cupric sulphate
Standard → it contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 100.5% calculated with reference to the dried substance at 250ׄ c.
Method of preparation–
2Cu+S+3O2 → CuSo4+2CuO
↓dil. H2SO4
2CuSO4 +H2O
Physical properties-
- It exists in the form of deep blue crystal of pentahydrate available in the form of granules or powder.
- It shows effervescence in dry air slowly.
- It is soluble in water, very soluble in boiling water and insoluble in alcohol.
Chemical properties-
- On heating at 100ׄ c it loses the water molecules and form anhydrous solution.
CuSo4.5H2O —100 ͦc—→ CuSo4.3H2O+2H2O —100 ͦc—→ CuSo4.2H2O+H2O
↓ 200 ͦ c
CuSO4[anhydrous salt]
- At very high temperature, it decomposes to cupric oxide and Sulphur dioxide gas.
2CuSo4→2CuO+So2+O2
Assay :- The principle involved in assay of copper sulphate is oxidation reduction reaction. This reaction is based on the instability of CUI formed in the reaction of copper sulphate with potassium iodide, which decomposes to give cuprous iodide with the liberation of free iodine.
2CuSo4+4KI→2CuI2+2K2SO4
2CuI2→Cu2I2+I2
2gm of potassium thiocyanate is then added and titrated until the blue colour disappears.
I2+2Na2S2O3→Na2S4O6+2NaI
Cu2I2+KCNS→2CuNS+2KI
Each 1 ml of 0.1N sodium thiosulphate ≡0.02497gm of CuSO4.5H2O
Identification test:- A 5% w/v sample solution of cupric sulphate is tested for copper and sulphate.
Test for purity:- 1.Chlorides not more than 100 ppm.
2.Iron not more than 10 ppm.
3.Lead not more than 50 ppm.
4.Loss on drying not more than 33-36.5%
Uses– 1. As emetics, but in large doses, it is corrosive in nature
2.chemical antidote in phosphorous poisoning
3.Externally it is astringent and fungicidal
4.It is ingredient of benedicts and Fehling’s reagent
Sodium potassium Tartrate (C4H4KNaO6 ∙ 4H2O)
Synonyms :- Rochelle salt
Seignette salt
PREPARATION :-
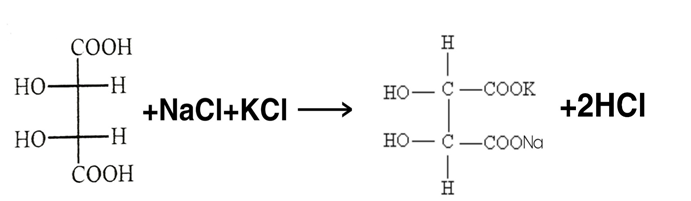
Tartaric acid Sodium potassium Tartrate
Physical properties-
It is crystalline powder, odourless freely soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol.
Chemical properties-
On heating, it gives odour of burning sugar.
C4H4O6KNa.4H2O+5O2→K2CO3+Na2CO3+8H2O+6CO2
Identification test:- As chemical properties
Storage:- Air tight container
Dose:- 10gm to adult
Uses:- 1. Saline cathartic.
2.Depending upon the dose, it is also used as mild laxative.
3. It can also be used as diuretic and urinary alkalizer.
4. It is used as food additive as a stabilizer in meat and cheese
Products.
5.It is an ingredient of compound effervescent powder.
HAEMATINICS
These are the agents which are required for the formation of blood cells and also used in the treatment of anemia. Eg. Ferrous sulphate, ferrous gluconate.
Anemia is decreased capacity of RBCs to carry oxygen to the tissues. It occurs when the balance between production and destruction of RBCs is disturbed. The disturbance can occur due to
- Blood cells
- Impaired red blood cell formation due to deficiency of essential factors i.e. Iron, vitamin B12, folic acid or bone marrow depression.
- Increased destruction of RBCs ( Hemolytic anemia )
Ferrous sulphate(FeSO4.7H2O)
Method of preparation
Fe+H2SO4→FeSO4+H2↑
Physical properties:-
It is odorless, bluish green crystal or powder, metallic taste and astringent. It is completely soluble in water and insoluble in alcohol.
Chemical properties:-
- On heating it decomposes to ferric oxide, Sulphur dioxide and Sulphur trioxide.
2FeSO4→Fe2O3+SO2+SO3
- It reduces to the salt of silver and gold to their corresponding metals.
Ag++Fe2+→Ag+Fe3+
Au3++3Fe2+→Au+3Fe3+
Storage:-Air tight containers
Assay:- principle-Redox titration
An accurately weighted 1g powder is dissolved in 20ml of dilute HCL. Then this solution is titrated against 0.1NKMn
10FeSO4+2KMnO4+8H2SO4→K2SO4+2MnSO4+5Fe2(SO4)3+H2O
Here KMnO4 solution acting as self indicator.
Each 1ml of 0.1NKMnO4≡0.0291gm of Feso4
Dose:- It is given in a dose of 300-400 mg daily.
Uses:– 1. It is used as hematinic.
2. It is used in the treatment of anemia caused by iron deficiency.
3. It also posses disinfectant property.
4. It is used as an insecticide in agriculture.
Caution:– 1.Excessive consumption by children may cause GIT irritation Or shock.
2.It may cause discoloration of teeth in contact.